Summer is the season for enjoying watermelon. Whether eaten alone or juiced, watermelon is a refreshing thirst quencher. With its high water content, watermelon is not only hydrating but also offers benefits such as promoting urination and lowering blood pressure. It has become one of the most popular fruits in summer. In this blog, we have compiled common questions about watermelon varieties, the benefits of eating watermelon, the calorie ranking of different types, and tips on how to choose a delicious watermelon, so that you can enjoy watermelon safely and healthily.
🍉What are the Types of Watermelon?
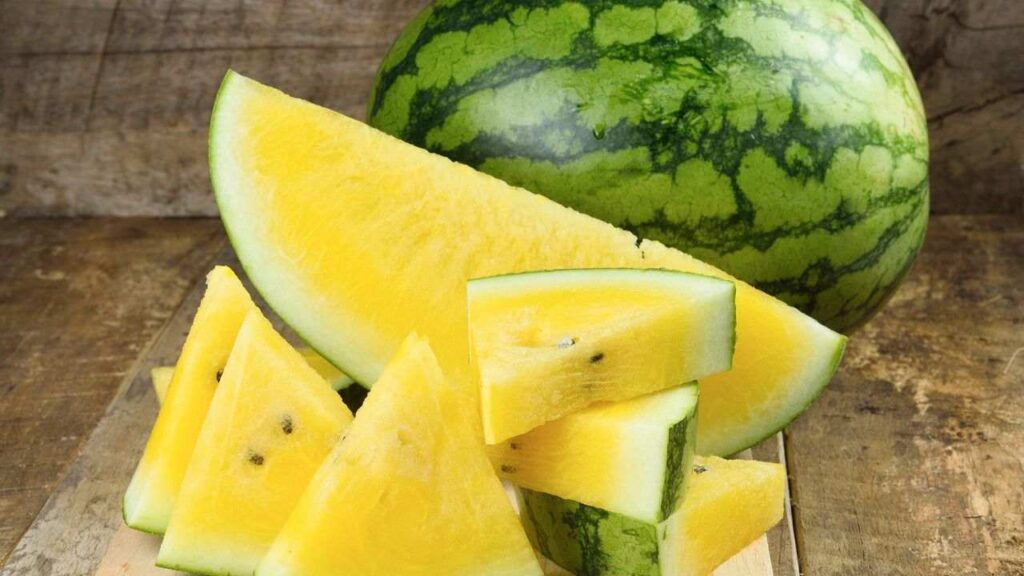
Watermelon is one of the indispensable fruits in summer. It has a deep green or light green rind and red or yellow flesh. The seeds can be black, white, or reddish. With a water content of 94%, watermelon is the cheapest and most hydrating fruit in summer. Watermelon can be divided into two types: “red flesh” and “yellow flesh.”

Red Flesh:
- Common large red flesh watermelon: It has a slightly grainy texture when eaten and common varieties include Black Diamond Watermelons and Jubilee Watermelons.
- Common small red flesh watermelon: Common varieties include Sugar Baby and the Tiger Baby.
- Yellow-skinned small watermelon: Common variety includes Diana.
Yellow Flesh:
- Common yellow or orange flesh watermelon: It has a crisp texture when eaten.
- Yellow-skinned orange flesh watermelon: It has a refreshing flavor when eaten.
- Common varieties include Desert King, Tender-gold, Yellow Baby, Yellow Doll.

🍉 What are the Benefits of Eating Watermelon?
Watermelon contains 94% water and minimal fat. However, its juice contains almost all the nutrients needed by the human body. Every 100 grams of watermelon contains 126.7 milligrams of vitamin A (the highest in red flesh), 0.05 milligrams of vitamin B1, 0.04 milligrams of vitamin B2, 0.04 milligrams of vitamin B6, phosphoric acid, and malic acid.
In addition, watermelon is rich in fiber, pectin, and lignin, which promote gastrointestinal motility. The rind and seeds of watermelon also contain nutrients. The white part of the rind contains abundant vitamin C and valuable compounds. Watermelon is known for its appetizing, digestion-aiding, thirst-quenching, cooling, diuretic, metabolism-promoting, and nourishing effects.

Speaking of watermelon, many people think of “Kodama” or “Baby Watermelon.” However, “Kodama” does not refer to a specific variety but to all yellow flesh watermelons. It was originally introduced from Japan, where “Kodama” means spherical or round shape. Nowadays, “Kodama” is used to refer to small watermelons.
🍉How to Select the Sweetest Watermelon?
Watermelon is refreshing and thirst-quenching, but how can you choose a sweet and juicy one? In fact, the selection technique for determining the sweetness of watermelon is based on its appearance and “tapping the rind.” It is recommended that you tap the rind before purchasing and choose a watermelon that produces a crisp and loud sound. Additionally, it is best to select watermelons with smooth and intact surfaces, bright green color, clear and distinct patterns, curly stems, and slightly sunken peduncle parts.
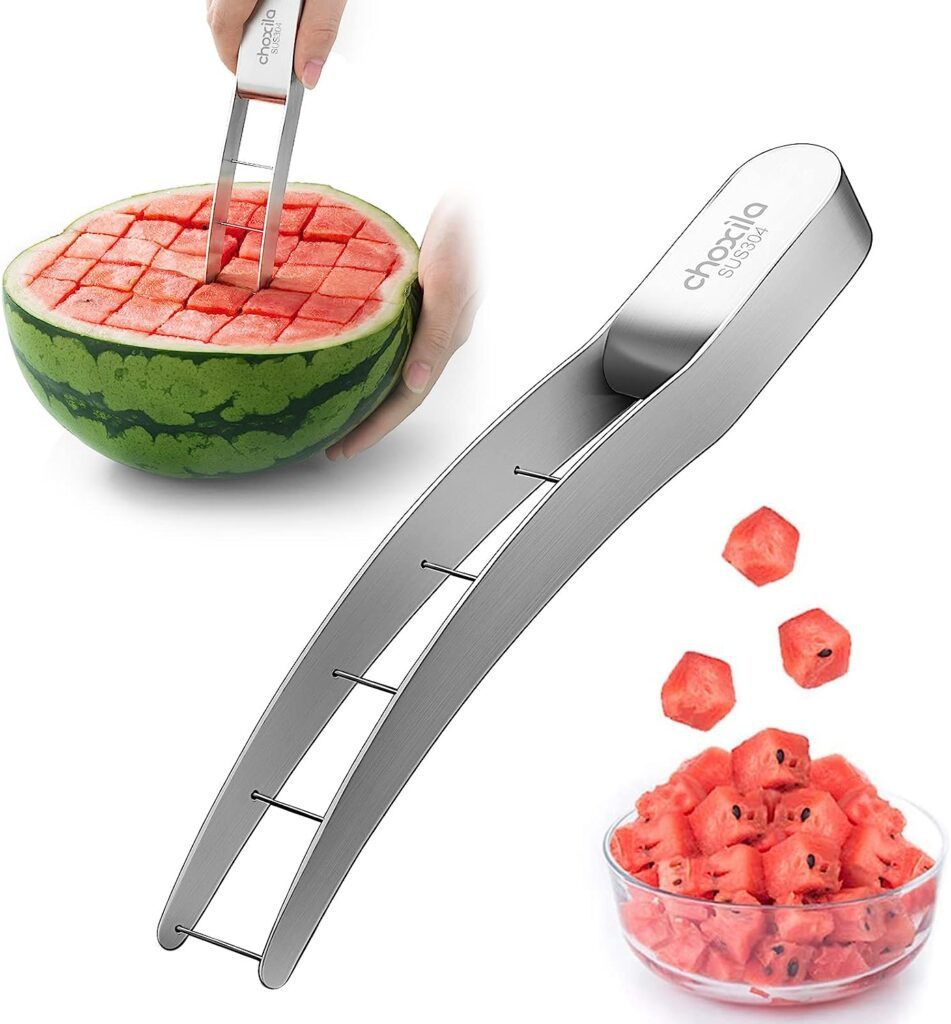


🍉How Long Can Watermelon Be Refrigerated?
We often see pre-cut watermelon in markets or night markets, but is it the right way to store it? If pre-cut watermelon is not eaten immediately or properly stored, it can be contaminated by bacteria or mold floating in the air. Using unclean cutting boards and knives can also easily transfer bacteria from the oral cavity to the watermelon, causing microbial contamination.

Even if the watermelon is wrapped in cling film or stored in a refrigerator, the risk of bacterial growth is still high if left for too long. It is recommended not to keep the watermelon wrapped in cling film for too long and consume it promptly.

🍉Calorie Ranking of Watermelon
Many people enjoy eating a few slices of watermelon in the summer to feel refreshed. However, did you know that the calorie content differs between different flesh types? In fact, red flesh watermelon has slightly higher calories than yellow flesh watermelon. Nutritionist also shared the calorie and nutritional content of watermelon with different flesh types on her Facebook page for reference.
Red Flesh Watermelon (Calories: 32 kcal):
Carbohydrates/Protein/Fat: 8g/0.8g/0.1g Dietary Fiber: 0.3g Potassium: 121mg Zinc: 0.2mg Vitamin A: 687 I.U. Beta-Carotene: 412μg Vitamin C: 6.8mg Citrulline: Low
Yellow Flesh Watermelon (Calories: 29 kcal):
Carbohydrates/Protein/Fat: 7.3g/0.7g/0.1g Dietary Fiber: 0.3g Potassium: 99mg Zinc: 0.3mg Vitamin A: 1mg Beta-Carotene: 1μg Vitamin C: 5.4mg Citrulline: High.


🍉Precautions for Eating Watermelon
Although eating watermelon in the summer can be cooling and thirst-quenching, it is not suitable for everyone. Despite its many benefits, there are also precautions to consider when consuming watermelon. Nutritionists point out that watermelon has a cooling nature, so individuals with poor kidney function or diabetes need to pay attention to their intake:
- Eating too much can lead to indigestion and diarrhea, so it is recommended to consume it in moderation.
- Individuals with poor kidney function: Due to the high potassium and water content in watermelon, potassium intake or fluid intake needs to be controlled.
- Individuals with diabetes: Although watermelon has a high glycemic index, its glycemic load (GL value, which represents the impact of a portion on blood sugar levels) is not high. For individuals with diabetes, as long as the portion size is controlled to one serving of fruit, the impact on blood sugar fluctuations will not be significant.